Page 56 - ODV Training outline_EN
P. 56
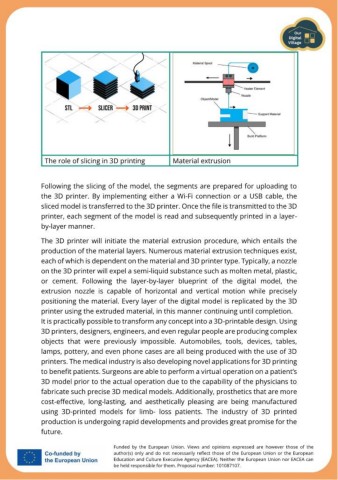
The role of slicing in 3D printing Material extrusion
Following the slicing of the model, the segments are prepared for uploading to
the 3D printer. By implementing either a Wi-Fi connection or a USB cable, the
sliced model is transferred to the 3D printer. Once the file is transmitted to the 3D
printer, each segment of the model is read and subsequently printed in a layer-
by-layer manner.
The 3D printer will initiate the material extrusion procedure, which entails the
production of the material layers. Numerous material extrusion techniques exist,
each of which is dependent on the material and 3D printer type. Typically, a nozzle
on the 3D printer will expel a semi-liquid substance such as molten metal, plastic,
or cement. Following the layer-by-layer blueprint of the digital model, the
extrusion nozzle is capable of horizontal and vertical motion while precisely
positioning the material. Every layer of the digital model is replicated by the 3D
printer using the extruded material, in this manner continuing until completion.
It is practically possible to transform any concept into a 3D-printable design. Using
3D printers, designers, engineers, and even regular people are producing complex
objects that were previously impossible. Automobiles, tools, devices, tables,
lamps, pottery, and even phone cases are all being produced with the use of 3D
printers. The medical industry is also developing novel applications for 3D printing
to benefit patients. Surgeons are able to perform a virtual operation on a patient’s
3D model prior to the actual operation due to the capability of the physicians to
fabricate such precise 3D medical models. Additionally, prosthetics that are more
cost-effective, long-lasting, and aesthetically pleasing are being manufactured
using 3D-printed models for limb- loss patients. The industry of 3D printed
production is undergoing rapid developments and provides great promise for the
future.
Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the
author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European
Education and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA). Neither the European Union nor EACEA can
be held responsible for them. Proposal number: 101087107.